To add CPU or memory resources to an existing GitHub Enterprise instance, shut down the instance and use the underlying virtual platform's tools to allocate the resources to the virtual machine. The newly allocated resources are automatically recognized on boot and no additional configuration is necessary.
Warning: The process for allocating new system resources varies by virtualization platform and resource type. You should always configure the monitoring and alerting of key system resources. For more information, see "Monitoring your GitHub Enterprise appliance."
In this guide
- Adding CPU or memory resources for AWS
- Adding CPU or memory resources for OpenStack KVM
- Adding CPU or memory resources for VMWare
Adding CPU or memory resources for AWS
Note: To add CPU or memory resources for AWS, you must be familiar with using either the AWS management console or the aws ec2 command line interface to manage EC2 instances. For background and details on using the AWS tools of your choice to perform the resize, see the AWS documentation on resizing an Amazon EBS-backed instance.
Resizing considerations
Before increasing CPU or memory resources for your GitHub Enterprise instance:
-
Verify that an Elastic IP is assigned to the instance
If an Elastic IP isn't assigned, you'll have to adjust the DNS A records for your GitHub Enterprise host after the restart to account for the change in public IP address. Once your instance restarts, the Elastic IP (EIP) is automatically retained if the instance is launched into a VPC. If the instance is launched into EC2-Classic, the Elastic IP must be manually re-associated.
-
Choose your new instance type
You need to determine the instance type you would like to upgrade to based on CPU/memory specifications. The following table lists instance types supported by GitHub Enterprise. For more information on the hardware specifications and costs associated with each instance type, see the AWS EC2 instance type overview page.
Instance type Family vCPU Memory m3.xlarge General purpose 4 15 GB m3.2xlarge General purpose 8 30 GB c3.2xlarge Compute optimized 8 15 GB c3.4xlarge Compute optimized 16 30 GB c3.8xlarge Compute optimized 32 60 GB r3.large Memory optimized 2 15 GB r3.xlarge Memory optimized 4 30 GB r3.2xlarge Memory optimized 8 61 GB r3.4xlarge Memory optimized 16 122 GB r3.8xlarge Memory optimized 32 244 GB
Resizing for AWS
Note: For instances launched in EC2-Classic, write down both the Elastic IP address associated with the instance and the instance's ID. Once you restart the instance, re-associate the Elastic IP address.
It's not possible to add CPU or memory resources to an existing AWS/EC2 instance. Instead, you must:
- Stop the instance.
- Change the instance type.
- Start the instance.
- Once the instance has fully restarted and you can reach it, use the SSH administrative shell to verify that the new resource configuration is recognized:
ssh -p 122 admin@HOSTNAME ghe-system-info
Adding CPU or memory resources for OpenStack KVM
It's not possible to add CPU or memory resources to an existing OpenStack KVM instance. Instead, you must:
- Take a snapshot of the current instance.
- Stop the instance.
- Select a new instance flavor that has the desired CPU and/or memory resources.
Adding CPU or memory resources for VMWare
If operations on your GitHub Enterprise instance are slow, you may need to add CPU or memory resources.
- Use the vSphere Client to connect to the VMware ESXi host.
- Shut down your GitHub Enterprise instance.
- Select the virtual machine and click Edit Settings.
- Under "Hardware", adjust the CPU and/or memory resources allocated to the virtual machine as needed:
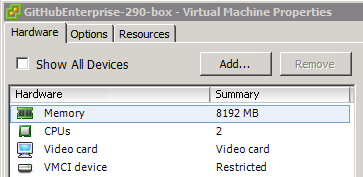
- To start the virtual machine, click OK.
- Once the instance has fully restarted and you can reach it, use the SSH administrative shell to verify that the new resource configuration is recognized:
ssh -p 122 admin@HOSTNAME ghe-system-info
